By comparing current variance figures with those from previous periods or those of competitors, analysts can identify trends and patterns that may indicate areas for improvement or the need for strategic adjustments. This benchmarking process can reveal whether a company is maintaining a competitive edge in terms of cost efficiency and capacity utilization. In conclusion, Fixed Overhead Volume Variance is crucial for cost management and decision-making. It provides valuable insights into the efficiency of a company in managing its fixed overhead costs and helps make informed decisions regarding production levels. By understanding the concept of FOVV and its importance, businesses can make informed decisions that positively impact their profitability and competitiveness. Fixed overhead expenditure variance is the difference between the budgeted fixed overhead expenditure and actual fixed overhead expenditure.
- When the cumulative amount of the variance becomes too large over time, a business should alter its budgeted allocation rate to bring it more in line with actual volume levels.
- When calculated using the formula above, a positive fixed overhead volume variance is favorable.
- Fixed overhead volume variance is positive when the applied fixed overheads exceed budgeted fixed overheads.
- If the fixed overhead cost applied to the actual production using the standard fixed overhead rate is bigger than the budgeted fixed overhead cost, the fixed overhead volume variance is the favorable one.
The fixed production overhead total variance can be subdivided as follows:
Calculate the fixed overhead spending and production volume variances using the format shown in Figure 10.13 “Fixed Manufacturing Overhead Variance Analysis for Jerry’s Ice Cream”. Sales Quantity Variance already takes into account the change in budgeted fixed production overheads as a result of increase or decrease in sales quantity along with other expenses. When calculated using the formula above, a positive fixed overhead volume variance is favorable. Beside from its role as a balancing agent, fixed overhead volume variance does not offer more information from what can be ascertained from other variances such as sales quantity variance. Fixed overhead volume variance refers to the difference between the budgeted fixed overheads and the actual overheads applied to the units produced during an accounting period. The variance value reflects the over or under absorption of fixed overheads, and it arises due to a change in the quantum of production against the budgeted quantum of production.
Formulas to Calculate Overhead Variances
If the actual amount spent on fixed overhead is not the same as the amount budgeted for fixed overhead, then there will be a variance known as the fixed overhead budget variance. When the cumulative amount of the variance becomes too large over time, a business should alter its budgeted allocation rate to bring it more in line with actual volume levels. This is obtained by comparing the total overhead cost actually incurred against the budgeted overhead cost i.e. The volume capacity variance is the difference between the budgeted hours of work and the actual active hours of work (excluding any idle time). Fixed overhead volume variance helps to ‘balance the books’ when preparing an operating statement under absorption costing.
Which of these is most important for your financial advisor to have?
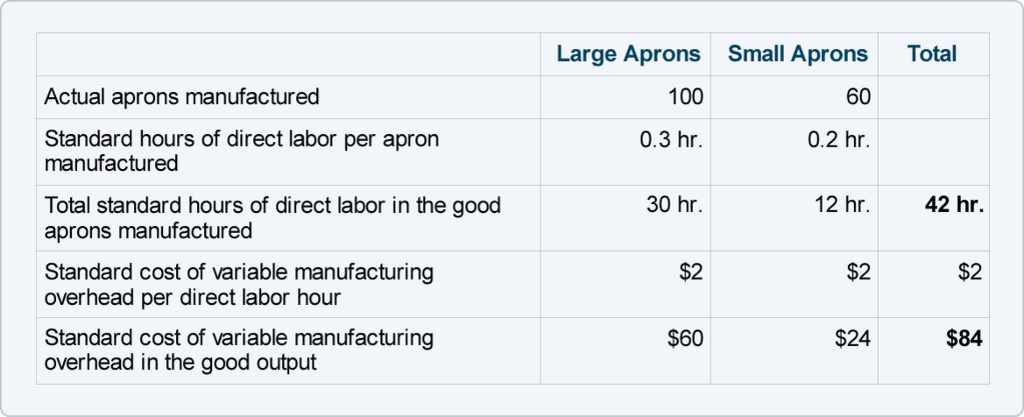
Nonetheless, we will assign the fixed manufacturing overhead costs to the aprons by using the direct labor hours. This is due to the actual production volume that it has produced in August is 50 units lower than the budgeted one. Recall that the fixed manufacturing overhead costs (such as the large amount of rent paid at the start of every month) must be assigned to the aprons produced.
Do you already work with a financial advisor?
The net variance from standard cost and the line items leading up to it build deviations from standard amounts right into the income statement. Managers can focus on discovering reasons for these differences to budget and operate more effectively in future periods. The standard cost per unit of $113.60 calculated previously is used to determine cost of goods sold – at standard amount. Since the expenditure is considered to be under the control of management, the overhead budget variance is referred to as a controllable variance. Increase or decrease in production due to more or less working days at the rate of revised capacity × Standard rate per unit. If the actual overheads are more, it shall result in an adverse variance and vice versa.
Role in Financial Analysis
A company budgets for the allocation of $25,000 of fixed overhead costs to produced goods at the rate of $50 per unit produced, with the expectation that 500 units will be produced. However, the actual number of units produced is 600, so a total of $30,000 of fixed overhead costs are allocated. The expectation is that 3,000 units will be produced during a time period of two months. However, the actual number of units produced is only 2,000, resulting in a total of $50,000 fixed overhead costs. When standard hours exceed normal capacity, the fixed factory overhead costs are leveraged beyond normal production.
In other words, each apron must absorb a small portion of the fixed manufacturing overhead costs. At DenimWorks, the fixed manufacturing overhead is assigned to the good output by multiplying the standard rate by the standard hours of direct labor in each apron. Hopefully, by the end of the year there will be enough good aprons produced to absorb all of the fixed manufacturing overhead costs. The actual product might be different, and therefore, it leads to a difference in the total fixed overheads absorbed or applied to the actual production and the budgeted fixed overheads.
For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) has worked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to help them make informed decisions for their individual needs. Finance Strategists is a leading financial education organization that connects people with financial professionals, priding learn more about a tax deduction vs tax credit itself on providing accurate and reliable financial information to millions of readers each year. This team of experts helps Finance Strategists maintain the highest level of accuracy and professionalism possible. At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content. The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice.
However, it could also raise concerns about overextension of resources and the potential for increased wear and tear on machinery, which could lead to higher maintenance costs or capital expenditures in the long term. This type of variance is calculated separately for direct variable expenses and overhead variable expenses. It is influenced by idle time, machine breakdown, power failure, strikes or lockouts, or shortages of materials and labor.
This variance shows the over or under absorption of fixed overheads during a particular period. If the actual output is more than the standard output, there is over-recovery of fixed overheads and volume variance is favorable and vice versa if the actual output is less than the standard output. Fixed overhead cost variance is the difference between the standard costs of fixed overhead allowed for the actual output achieved and the actual fixed overhead cost incurred i.e. Fixed Overhead Volume Variance is necessary in the preparation of operating statement under absorption costing as it removes the arithmetic duplication as discussed earlier. The variance is favorable because Motors PLC managed to operate more manufacturing hours than anticipated in the budget. The variance is adverse because Motors PLC utilized more manufacturing hours in the production of 275,000 units than the standard.
